Control Valve Actuator Component and function
The control valve is a general term for devices that configure the valve and actuator of the body, operate the valve using the controller of the operation part, and consequently adjust the amount of Process corresponding to it.
With the control valve the actuator has an important function to determine the position of the valve plug. In process, successful process control can be executed depending on how to maintain appropriate valve plug position selection.
Control Valve Construction
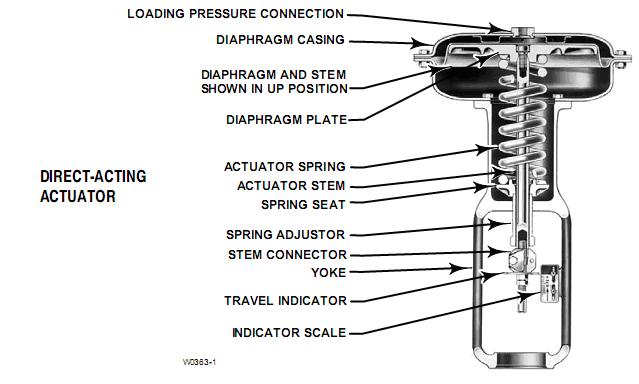 |
| <Figure 1 Control Valve Actuator Components> |
Instrument place where pneumatic air or gas enters.
2. Diaphragm Casing
It is divided into an upper casing and a lower casing and serves as a casing for Diaphragm.
3. Diaphragm and stem shown in up position
Diaphragm is a term for diaphragm, it is a part which practically controls valve positioning while moving in the upper and lower directions by Loading pressure as a movable part driven by fluid (air and gas).
Circular plate assembled with diaphragm
5. Actuator Spring
When the supply of loading pressure is interrupted, Actuator spring restores the position of the valve and plays a role. It is called the Failure position and the Fail position therefore the spring position is different.
- Fail close valve: Actuator spring position is located under Loading pressure
- Fail open Valve: Actuator spring position is located on Loading pressure
6. Actuator Stem
It is the axis that plays a role of transmitting diaphragm motion to Valve plug and Valve stem. It is connected to the diaphragm plate.
7. Spring seat
Secure the actuator spring.
8. Spring adjustor
Spring position adjuster, installed in the actuator body with screws, connected to the Spring seat. It is a device which adjusts compression of Spring.
9. Yoke
It is a section connected to the valve main body, and it is configured in the form of wrapping around the operation part.
10. Travel indicator & Scale
The travel indicator consists of a thin metal plate and is installed in Valve stem.
Scale is installed in the Yoke part and is a device to confirm how the valve is opened and closed with the scale installed.
Control Valve Actuator Operating Principle
How does the control valve work?
There are Valve Plug and Valve Stem in the upper direction with reference to the Inlet port and Outlet port of the valve. Valve Plug performs the role of opening and closing the flow of fluid. The Control valve is divided into Spring and Diaphragm, Plug, Solenoid valve roux. When Air and Gas are applied according to the fixed pressure through Loading pressure connection, the diaphragm (Diaphragm) will operate while expanding downward. At this time, the position is changed by spring and pressure, and finally Valve Plug will operate through Seat. When air is exhausted through reverse loading pressure, the diaphragm will move upwards by Spring and will take action that Valve plug is opened. It is the pressure to control this, and as a result it determines the Valve plug positioning. For example, if half pressure of 7.5 psig is applied to the diaphragm, assuming that the pressure on the diaphragm is 100% Close, assuming that 15 psig of pressure is required, the valve plug's Position or 50% open / It means to be closed.
Main function of actuator
The main functions of the actuator are as follows.- The actuator must overcome the friction between Seal and Parking and be able to overcome the forces generated when the fluid moves from the valve so that the position of the Valve plug can be aligned with the Setting value.
- When the Valve plug is moved to position it must overcome the fluid force generated in the coffin and be able to maintain Positioning.
Actuator Fail Mode
Using loading pressure connection to the actuator, it refers to determining Valve position when received Pneumatic power is interrupted.
- Fail Open: When Pneumatic power supply is interrupted, the Valve plug will maintain the full open state. Actuator Spring moves Diaphragm in the upper direction. Direct-Acting method: When Loading pressure air is applied from the top to the diaphragm as shown in Fig. 2 below, the Spring force is a type sticking the diaphragm upward. Therefore it switches to Open in Fail state.
 |
| <Figure 2. Direct Acting> |
- Fail Close: Valve plug will remain fully closed when pneumatic power supply is interrupted. Reverse-acting method: As shown in the picture below, the spring force is pulling down the diaphragm that the loading pressure air is applied from Therefore, the bottom to the top with respect to the diaphragm diaphragm. Therefore, switch from Fail to Close.
 |
| <Figure 3. Revers Acting> |
By Plant Inside.




0 댓글